
Unless your users are using a credential manager, they have to enter their credentials each time. For smaller projects that require a less robust solution, PATs are a simple alternative. We recommend that you review our authentication guidance to help you choose the correct authentication mechanism. To set up PATs for non-Microsoft tools, use Git credential managers or create them manually.

#Decode base64 command line mac how to#
In this article, we show you how to create, use, modify, and revoke PATs for Azure DevOps.
#Decode base64 command line mac password#
You can use a personal access token (PAT) as an alternate password to authenticate into Azure DevOps. In this tutorial, you learned how to base64 encode files and strings.Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019 | TFS 2018 base64 -decode /path/to/file > output.txt Conclusion You may want to output stdout directly to a file. base64 -decode /path/to/fileĪs with encoding files, the output will be a very long string of the original file.
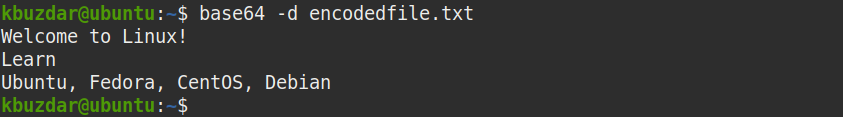
To decode a file with contents that are base64 encoded, you simply provide the path of the file with the -decode flag. Provided your encoding was not corrupted the output should be your original string. Using the example encoding shown above, let’s decode it back into its original form. With encoded string, you can pipe an echo command into base64 as you did to encode it. To decode with base64 you need to use the -decode flag. bas64 /path/to/file > output.txt Decoding Strings You may want to write the stdout to file instead. This will output a very long, base64 encoded string. To base64 encode a file base64 /path/to/file Which will output the following bXktc3RyaW5n Without the -n flag you may capture a hidden characters, like line returns or spaces, which will corrupt your base64 encoding. To ensure no extra, hidden characters are added use the -n flag. To base64 encode string you can pipe an echo command into the base64 command-line tool. While it may obfuscate that actual data from should surfers, anyone who has access to base64 encoded data can easily decode it. Rather it is a useful way of transferring or storing large data in the form of a string. Base64 is not EncryptionĮncoding files is not encryption and should never be used to secure sensitive data on disk. In short, base64 encoding ensures the integrity of our data when transferred over the network. The reason is ASCII files are string converted to bytes, and when those bytes are decoded incorrectly back to ASCII your data becomes corrupt.īase64 was introduced as a way to convert your ASCII data into arbitrary bytes, where they could then be transferred as bytes, and decoded correctly back to ASCII. Transferring an ASCII file over the network can cause corruption if not decoded correctly. OSX also comes bundled with its own version of base64. You should not have to perform any additional steps. If you are running popular linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, or Red Hat, the base64 command-line tool is typically pre-installed.

How to base64 encode on Ubuntu, Debian, OSX, and Red Hat One being is ensuring data integrity when transferring data over the network, while another is storing Secrets in Kubernetes.Īfter reading this tutorial you will understand how to easily encode files or strings, and then decode them back. You will also learn what base64 encoding is and why it should never be used to protect data from unauthorized access.īase64 encoding and decoding data has many use cases. In this tutorial, you will learn how to base64 encode and decode from the command-line on Linux.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
